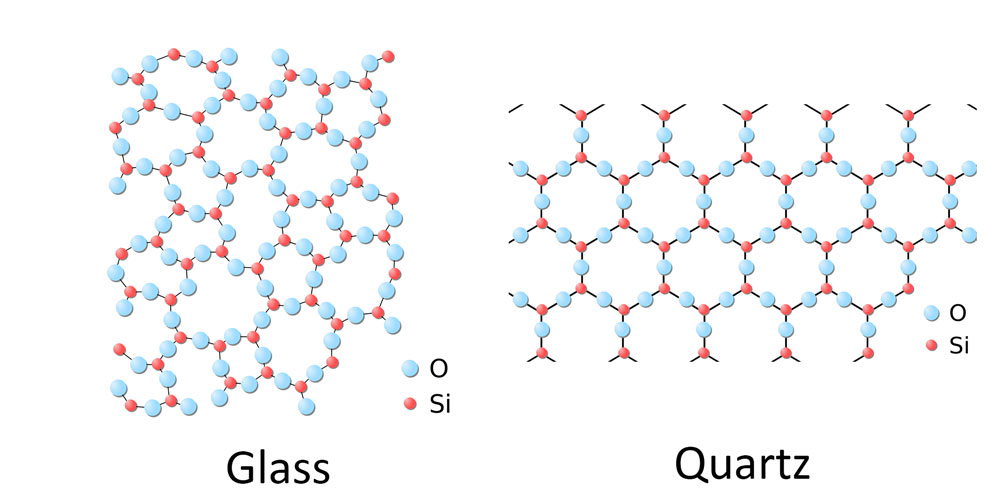
Glass Crystal Structure . Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen? • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances, and polyhedral connectivity) is. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. A glass, by definition, lacks an organized lattice or. the strong covalent bonds that exist between the atoms of inorganic glasses plus the lack of crystal structure give glass. Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz.
from mungfali.com
Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen? a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. the strong covalent bonds that exist between the atoms of inorganic glasses plus the lack of crystal structure give glass. Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. A glass, by definition, lacks an organized lattice or. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances, and polyhedral connectivity) is. • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass.
Atomic Structure Of Glass
Glass Crystal Structure a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. A glass, by definition, lacks an organized lattice or. a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. the strong covalent bonds that exist between the atoms of inorganic glasses plus the lack of crystal structure give glass. • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances, and polyhedral connectivity) is. Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen?
From theatrotour.com
7 Types Of Crystal Structures Tout Ce Que Vous Devez Savoir Glass Crystal Structure the strong covalent bonds that exist between the atoms of inorganic glasses plus the lack of crystal structure give glass. Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen? glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances, and polyhedral connectivity) is. • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. Structures of a typical. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.friendsofglass.com
What is the difference between glass and crystal? Friends of Glass Glass Crystal Structure glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances, and polyhedral connectivity) is. Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. A glass, by definition, lacks an organized lattice or. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.pnas.org
Molecular dynamics simulations of liquid silica crystallization PNAS Glass Crystal Structure the strong covalent bonds that exist between the atoms of inorganic glasses plus the lack of crystal structure give glass. Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration. Glass Crystal Structure.
From winesutra.in
Crystal vs Glass Winesutra Glass Crystal Structure Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances, and polyhedral connectivity) is. Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen? glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.toppr.com
Crystalline and Amorphous Solids Explanation, Differences, Examples, etc Glass Crystal Structure Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.).. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.victoriana.com
Pack Lotus Palme las glass ceramic Reise bilden Eis Glass Crystal Structure glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen? the strong covalent bonds that exist between. Glass Crystal Structure.
From emoryinsiena2012.blogspot.com
Chemistry Studies in Siena 2012 Lead Oxide Exploring the difference Glass Crystal Structure glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances, and polyhedral connectivity) is. • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.britannica.com
Hexagonal closepacked structure crystallography Britannica Glass Crystal Structure Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. A glass, by definition, lacks an organized lattice or. glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances,. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.mdpi.com
Crystals Free FullText Structure and Anharmonicity of α and β Glass Crystal Structure Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). A glass, by definition, lacks an organized lattice or. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. the strong covalent bonds that. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 13 States of Matter PowerPoint Presentation, free Glass Crystal Structure A glass, by definition, lacks an organized lattice or. • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.researchgate.net
Several examples of natural photonic crystals with various structural Glass Crystal Structure A glass, by definition, lacks an organized lattice or. Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen?. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.geologyin.com
Crystal Structure and Crystal Systems Glass Crystal Structure Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. the strong covalent bonds that exist between the atoms of inorganic glasses plus the lack of crystal structure give glass.. Glass Crystal Structure.
From mungfali.com
Glass Crystal Structure Glass Crystal Structure • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. A glass, by definition,. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.beautifulchemistry.net
Crystal Structure — Beautiful Chemistry Glass Crystal Structure Structures of a typical solid (l.) and glass (r.). a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. the strong covalent bonds that exist between the atoms of inorganic glasses plus the lack of crystal structure give glass. Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.dreamstime.com
Blue Realistic Glass Crystal Diamond Structure Background Vector Glass Crystal Structure Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen? Structures of. Glass Crystal Structure.
From mungfali.com
Atomic Structure Of Glass Glass Crystal Structure • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen? Common form of silica is sand, but it also occurs in nature in a crystalline form known as quartz. glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances, and polyhedral connectivity) is. the strong covalent bonds that. Glass Crystal Structure.
From www.researchgate.net
Crystal structure illustration and transmission electron microscopy Glass Crystal Structure Brow glass structure (1) importance of zachariasen? • first to apply crystal chemical principles to the study of glass. glass structure (i.e., cation coordination number, oxidation states and bonding distances, and polyhedral connectivity) is. A glass, by definition, lacks an organized lattice or. the strong covalent bonds that exist between the atoms of inorganic glasses plus the lack. Glass Crystal Structure.
From chem.libretexts.org
Crystalline Solid Structures Chemistry LibreTexts Glass Crystal Structure a 'phonon' is a collective organized vibration or excitation of atoms in a periodic lattice. glasses do not exhibit the ordered crystalline structure of most other ceramics but instead have a highly disordered amorphous. the strong covalent bonds that exist between the atoms of inorganic glasses plus the lack of crystal structure give glass. Brow glass structure. Glass Crystal Structure.